Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-25 Origin: Site









Eye bolts play a crucial role in securing and lifting heavy loads safely. Have you ever wondered which type of eye bolt is best for your specific application?
In this article, we will explore the three main types of eye bolts—shouldered, non-shouldered, and forged/bent. We’ll dive into their unique design features and applications to help you choose the right one for your needs.
By the end, you'll understand how to select the ideal eye bolt for your rigging and lifting tasks, ensuring both safety and efficiency.
An eye bolt is a type of fastener with a loop at one end and a threaded shaft at the other. The threaded part is inserted into a surface, such as wood, metal, or concrete, while the loop provides a connection point for lifting or securing equipment. Eye bolts are commonly used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, and marine, where they facilitate the lifting of heavy loads, anchoring, and securing equipment.
These bolts come in various designs to accommodate different applications and load types. The right type of eye bolt can ensure the safe and efficient handling of loads, while the wrong choice could result in accidents or equipment damage.
Eye bolts are used for a variety of purposes, with the primary goal being to secure or lift loads. Some of the most common applications include:
● Lifting and Rigging: Eye bolts are often used to attach slings or hoists to heavy equipment, such as beams, machinery, or containers. These bolts are designed to handle both vertical and angular lifting.
● Anchoring and Securing: Eye bolts can also serve as anchoring points for securing cables, ropes, or chains to structures. They are often seen in construction sites, warehouses, and marine environments.
● Marine Applications: In the marine industry, eye bolts are used for securing anchors, cables, and other equipment on boats, ships, or docks. Their corrosion-resistant properties make them ideal for this environment.
● Industrial Machinery: Eye bolts are commonly installed in industrial machinery to allow for lifting or maintenance. They provide a safe, sturdy attachment point for hoisting equipment during maintenance procedures.

Shouldered eye bolts are designed with a shoulder between the loop (eye) and the threaded shank. This feature helps to distribute the load more evenly, reducing the stress on the bolt when used in applications with side or angular loads. As such, shouldered eye bolts are particularly useful in heavy-duty lifting situations and are safe for both vertical and angled lifting.
These eye bolts are commonly used in situations where the load may not hang vertically, such as in construction or material handling applications. For an angled lift, it is crucial that the shoulder of the eye bolt is properly seated, ensuring that it maintains its strength and stability. Shouldered eye bolts offer superior load-bearing capacity compared to non-shouldered models, making them suitable for applications that involve dynamic or side loads.
Non-shouldered eye bolts, often referred to as plain pattern eye bolts, lack the shoulder between the loop and the shank. This design makes them suitable only for vertical lifting, where the load is applied directly in line with the bolt’s axis. Unlike shouldered eye bolts, non-shouldered eye bolts are not designed to handle angular loading, and using them in such applications can result in bending, breaking, or failure of the bolt.
It is important to ensure that non-shouldered eye bolts are used only for vertical lifts and that the load is aligned with the bolt’s axis. These bolts are typically found in lighter-duty applications where the risk of side loading is minimal, such as in securing cables or light equipment.
Eye bolts can also be categorized based on how they are manufactured. The two main methods are forging and bending. Forged eye bolts are made by hammering or pressing metal into shape, which results in a stronger and more durable product. These bolts are ideal for heavy-duty applications and can handle higher load capacities than bent eye bolts.
Bent eye bolts, on the other hand, are formed by bending a solid rod into shape. While they are less expensive and simpler to produce, they are best suited for lighter-duty tasks where the load is not excessively heavy. Bent eye bolts should not be used in applications where angular loading is involved, as they lack the structural integrity needed to withstand such forces.
Type | Design Features | Suitable Use | Advantages | Limitations |
Shouldered | Shoulder between eye and shank | Vertical and angular lifts | Can handle side loads | Must be seated correctly for angular lifts |
Non-Shouldered | No shoulder, plain design | Vertical lifts only | Simpler, cost-effective | Cannot handle side or angular loads |
Forged/Bent | Forged from metal or bent from a rod | Heavy-duty or light-duty | Stronger (forged), cost-effective (bent) | Bent bolts not suitable for heavy loads |
When selecting an eye bolt for a specific application, several factors must be considered. First, you need to assess the weight and direction of the load. If the load is vertical and in-line, a non-shouldered eye bolt may be sufficient. However, if the load will be subjected to side or angular forces, a shouldered eye bolt is necessary to ensure the bolt can handle the stress without breaking or deforming.
Material compatibility is another critical factor. For outdoor or marine environments, corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or galvanized steel are ideal. In high-stress or high-temperature conditions, forged eye bolts made from alloy steel may be required for optimal strength and durability.
One of the most common mistakes when selecting eye bolts is using non-shouldered eye bolts for angular loads. These bolts are designed for vertical loads only, and subjecting them to side or angular forces can lead to failure. Another mistake is failing to account for the material strength and working load limits of the eye bolt. Each type of eye bolt has a specific weight capacity, and exceeding that capacity can result in serious accidents.
To avoid these mistakes, always verify the specifications of the eye bolt before use. Ensure that it is appropriate for the load type and that it meets the necessary strength requirements.
Proper installation and use of eye bolts are critical to ensuring safe lifting operations. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for installation, including ensuring that the bolt is properly seated and torqued to the required specifications. For angled lifts, ensure that the sling or lifting gear is aligned with the eye bolt to prevent unnecessary stress on the bolt. Regularly inspect eye bolts for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage, and replace any bolts that show signs of weakness.
Forged eye bolts are typically the strongest and most durable option. The forging process aligns the grain structure of the metal, resulting in a bolt that can withstand higher loads. In comparison, bent eye bolts, while less expensive and simpler to produce, are better suited for lighter-duty applications and are not as durable under heavy loads or angular stress.
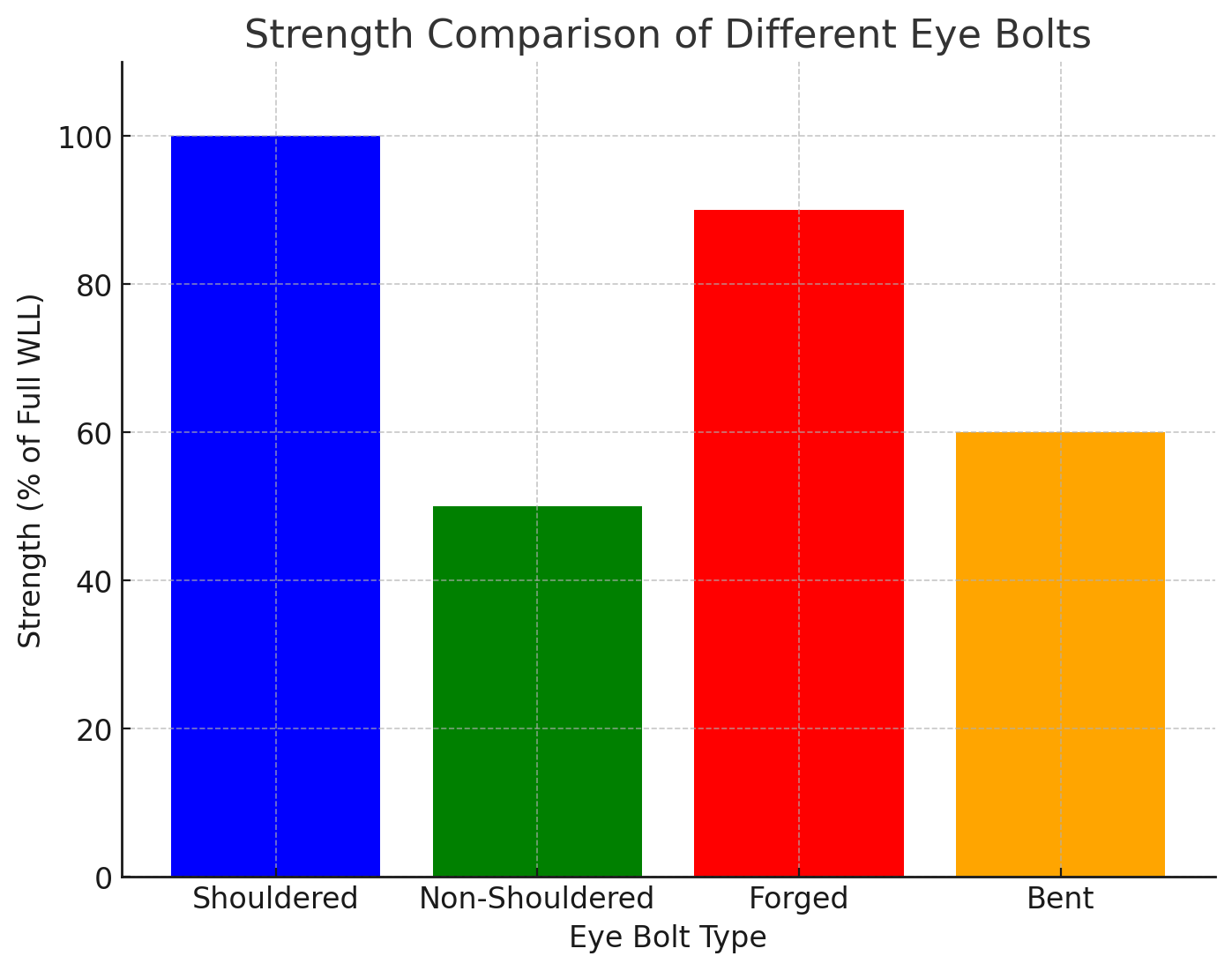
Each type of eye bolt has its own working load limit (WLL). Shouldered eye bolts have a higher WLL and can handle both vertical and angular loads. Non-shouldered eye bolts are limited to vertical lifting only and should not be used for angled lifts. Forged eye bolts are capable of handling the heaviest loads and are suitable for applications that require significant strength and durability.
While forged eye bolts are the most durable and offer the highest load capacity, they tend to be more expensive than bent or non-shouldered eye bolts. However, the added cost is justified when dealing with heavy-duty or high-risk lifting operations. Bent eye bolts, on the other hand, are cost-effective and ideal for lighter tasks but should never be used for heavy lifting or angled loads.
Eye Bolt Type | Typical Cost Range | Suitable for | Advantages |
Shouldered | Higher | Heavy-duty and side-loads | Greater strength and stability |
Non-Shouldered | Lower | Vertical lifts | More affordable |
Forged | Higher | Heavy-duty lifting | Durability and strength |
Bent | Lower | Light-duty tasks | Cost-effective for light loads |
Stainless steel eye bolts are highly corrosion-resistant, making them ideal for use in marine or outdoor environments where exposure to moisture and corrosive elements is a concern. These bolts maintain their strength and durability even when scratched or damaged, ensuring long-term reliability.
Galvanized eye bolts are coated with a layer of zinc to protect them from corrosion. This makes them suitable for use in less harsh environments where the risk of rusting is still present but not as severe as in marine applications. The galvanization process adds an extra layer of protection, making these bolts a reliable option for general outdoor use.
Swivel eye bolts are designed to rotate, allowing for the attachment of lifting slings or cables at various angles. This feature helps to reduce the strain on both the eye bolt and the rigging system, making them ideal for applications that require the load to move or change direction during lifting.
The working load limit (WLL) of an eye bolt decreases when subjected to angular loading. For instance, a shoulder eye bolt may lose up to 50% of its load capacity when used at an angle greater than 45 degrees. This is due to the additional forces exerted on the bolt when it is not aligned with the load. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for the WLL reduction when using eye bolts at an angle.
To calculate the WLL of an eye bolt, consider the type of load (vertical or angular), the material of the eye bolt, and its design features. Manufacturers typically provide specific load limits for their eye bolts, and it’s crucial to select the appropriate bolt for your application to ensure safety.
Choosing the right eye bolt is crucial for safety and preventing equipment failure. Understanding the differences between shouldered, non-shouldered, and forged/bent eye bolts helps ensure the right choice for lifting, securing, and handling materials. Regular maintenance, correct installation, and safety checks are vital. At Ningbo Weifeng Fastener Co., Ltd., we provide high-quality eye bolts designed for durability and reliability, helping you maintain efficient and safe operations in demanding environments.
A: The three main types of eye bolts are shouldered, non-shouldered, and forged/bent eye bolts. Each type serves different purposes depending on the load and lifting requirements.
A: A triangle eye bolt, typically used for specific rigging applications, has a triangular-shaped loop for added stability. It differs from traditional round eye bolts in design, making it suitable for unique lifting scenarios.
A: Shouldered eye bolts are ideal for both vertical and angular lifting. They are designed to withstand side loads, making them perfect for heavy-duty or side-loading applications.
A: No, non-shouldered eye bolts are designed for vertical lifting only. Using them for angled lifts could cause failure due to the lack of load distribution.
A: Forged eye bolts are stronger, more durable, and better suited for heavy-duty applications compared to bent eye bolts, which are used for lighter tasks.
A: Triangle eye bolts can be more specialized and may come at a higher price, depending on the application, compared to standard eye bolts. However, their unique design offers additional stability in certain lifting operations.


